Efficient probabilistic planar robot motion estimation given pairs of images
Olaf Booij, Ben Kröse and Zoran Zivkovic
Abstract
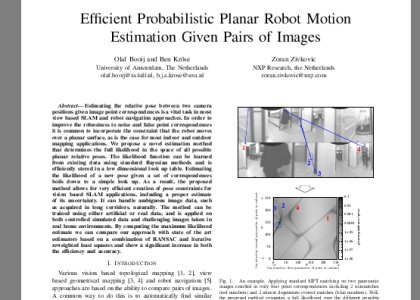
Estimating the relative pose between two camera positions given image point correspondences is a vital task in most view based SLAM and robot navigation approaches. In order to improve the robustness to noise and false point correspondences it is common to incorporate the constraint that the robot moves over a planar surface, as is the case for most indoor and outdoor mapping applications. We propose a novel estimation method that determines the full likelihood in the space of all possible planar relative poses. The likelihood function can be learned from existing data using standard Bayesian methods and is efficiently stored in a low dimensional look up table. Estimating the likelihood of a new pose given a set of correspondences boils down to a simple look up. As a result, the proposed method allows for very efficient creation of pose constraints for vision based SLAM applications, including a proper estimate of its uncertainty. It can handle ambiguous image data, such as acquired in long corridors, naturally. The method can be trained using either artificial or real data, and is applied on both controlled simulated data and challenging images taken in real home environments. By computing the maximum likelihood estimate we can compare our approach with state of the art estimators based on a combination of RANSAC and iterative reweighted least squares and show a significant increase in both the efficiency and accuracy.
Downloads
Download the final version from the rss site: pdf (717 kb).
Here are the slides I used during my presentation: pdf (6.7 mb).